Laser micromachining equipment manufacturers explain what cutting basic knowledge must be mastered
(Click 515 )Laser cutting was first used in the 1970s, after years of development, laser cutting has been widely used in sheet metal, ceramics, glass, semiconductors, plastics, wood, paper, cloth, all kinds of precision stainless steel pipes, plate processing.
When the high energy laser beam irradiates to the surface of the material, the rapid rise in temperature causes the material to instantly vaporize or melt before being blown away, and the laser beam moves along the contour line specified by the system to achieve the purpose of cutting. Like the current femtosecond laser with the most technical content, not only the cutting quality is high, the cutting slit is small, and the cutting accuracy is up to 5um, it has been widely used in the micro-machining of precision instruments such as medical devices, semiconductor integrated circuits, and electronic 3C.
Flame cutting is a standard process primarily used to cut mild steel, with oxygen as its main gas, which is pressurized to up to 6 bar and then blown into the cut. The heated metal reacts with oxygen: it begins to burn and oxidize. The chemical reaction releases a large amount of energy (up to five times the energy of the laser) to assist the laser beam in cutting.
Melting cutting is also a standard process for cutting metals and is mainly used for cutting soluble materials such as ceramics. The fusion cutting uses nitrogen or argon as the cutting gas, and the gas pressure of 2-20 bar is blown through the incision. Because these two gases are inert gases, they do not react with the molten metal in the incision and blow away directly. At the same time, the use of these two gases can also protect the cutting edge from air oxidation. There is also a melting cutting called compressed air cutting, which can also be used to cut thin sheets. Air pressurization to 5-6 bar is sufficient to blow away molten metal in the incision.
When the parameters are selected properly, plasma clouds will appear in the cutting incision. The plasma cloud consists of ionized metal vapor and ionized cutting gas. The plasma cloud absorbs the energy of the CO2 laser and converts it into the workpiece, allowing more energy to be coupled to the workpiece, and the material to melt faster, resulting in faster cutting. Therefore, this cutting process is also called high-speed plasma cutting. Plasma clouds are actually transparent relative to solid lasers, so plasma-assisted melting cutting can only be done with CO2 lasers.
The advantage of gasification cutting is to minimize the thermal effect on the surrounding materials, the cutting melt evaporates, low heat, high absorption materials can achieve the above effect, such as thin plastic film and wood, paper, foam and other non-melting materials. Ultrashort pulsed lasers allow the technique to be applied to other materials. The free electrons in the metal absorb the laser and heat up violently. The laser pulse does not react with the molten particles and plasma, and the material sublimates directly, during which energy cannot be transferred to the surrounding material in the form of heat. There is no obvious thermal effect when the picosecond pulse ablates the material, no melting and burr formation.
Laser processing parameter adjustment process: Many parameters affect the laser cutting process, some of which depend on the technical performance of the laser and the machine tool, while others are variable.
Degree of polarization: The degree of polarization indicates what percentage of the laser is being converted. The typical degree of polarization is around 90%. This is sufficient for a high-quality cut.
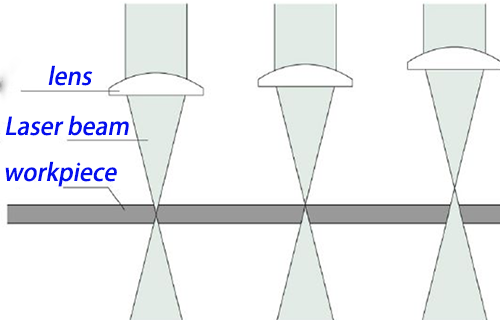
Focus diameter: The focus diameter affects the width of the incision. The focus diameter can be changed by changing the focal length of the focusing mirror. The smaller the focus diameter, the narrower the relative cutting.
Focus position: The focus position determines the beam diameter and power density on the workpiece surface as well as the shape of the cut.
Laser power: The size of the laser power is generally mainly matched with the type of processing, material thickness and material type. Can not be too high or too low, will marketing cutting quality and cutting efficiency.
Working mode: Continuous mode is mainly used to cut standard contours of metal and plastic in millimeter to centimeter size. In order to melt perforations or more precise profiles, a low-frequency pulsed laser is required.
Cutting speed: laser power and cutting speed match each other, too fast or too slow will lead to cutting quality problems, such as more burrs and other problems.
Nozzle diameter: The diameter of the nozzle determines the flow of gas and the shape of the air flow from the nozzle. The thicker the material is, the larger the diameter of the gas jet is, and the diameter of the corresponding nozzle opening is also increased.
Gas purity and pressure: Oxygen and nitrogen are often used as cutting gases. The purity and pressure of gas affect the cutting effect. When oxygen flame cutting is used, the purity of the gas needs to reach 99.95%. The thicker the steel plate, the lower the gas pressure used; When using nitrogen melt cutting, the gas purity needs to reach 99.995 percent (ideally 99.999 percent), and higher air pressure is required when melting and cutting thick steel plates.
Technical parameter table: In the early stage of laser cutting, the operator must adjust the setting of processing parameters by test run. Now the system can store the mature processing parameters or work according to the parameters set by the system. Mature laser cutting CNC system even novice can quickly skilled operation of laser cutting equipment.
Welcome to visit the official website of Men-Luck, a professional laser equipment manufacturer. We regularly organize laser-related knowledge and update it on the website. We hope to help more customers understand the professional knowledge of laser micro-processing equipment.
 WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: Wechat
Wechat
European customers purchase laser equipments again and put them into use! 2024-12-23
A chance encounter at the train station in 2023, with enthusiastic help, allowed us to meet European customers. After in-depth communication, the final customer purchased a laser welding machine and a laser marking machine, successfully completing the first cooperation between t…
Men-Luck has came to the HANNOVER MESSE 2024-04-26
It is reported that the 2024 Hannover MESSE in Germany has more than 1,000 Chinese enterprises participating in the sea, the scale of the exhibition is second only to the host Germany, and Chinese enterprises are accelerating their integration into the global industrial chain sy…
Ultraviolet laser cutting copper foil 2024-04-18
Metal foil is a thin sheet extended by metal, and ultra-thin metal foil has a variety of applications in various industries. Titanium foil can be used in loudspeaker components and medical equipment enclosures; Materials such as tungsten and molybdenum can be used for electronic…
The 2024 Munich laser world of photonics was successfully concluded 2024-03-22
In March 2024, the three-day Munich laser world of photonics has come to a perfect end in Shanghai, which has been held in Shanghai since 2006. As an important annual event for the laser, optical and photoelectric industries in Asia, the new edition of the fair covers the photoe…