Application of laser cutting in medical stent
(Click 1,329 )The stent belongs to the third category of medical devices, that is, the highest level of medical devices. It is a slender metal grid, very small, with a diameter of 2 ~ 4 mm, a few centimeters long, hollow, cylindrical, mesh metal tube.
Simply put, its principle is “to install a small stent into the blood vessel, open the narrow part, and maintain the smooth blood flow in the lumen. At present, stents include medical stainless steel, nickel titanium alloy, magnesium titanium alloy, cobalt chromium alloy, soluble metal magnesium, biodegradable polymers and other products; according to the placement location, they can be divided into coronary stents, cerebrovascular stents, renal artery stents, arterial stents, etc.
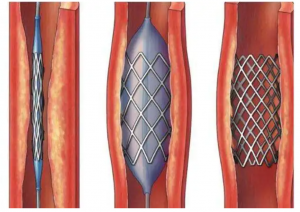
How are vascular stents processed?
Because the wall tube of cardiac stent is extremely thin, microsecond fiber laser is used in the mainstream stent cutting. However, because laser processing itself is thermal processing, melting the metal with laser and blowing it away with high-pressure gas will not only leave a lot of molten slag and burrs after processing, but also the heat during processing is easy to oxidize the surface of the support to make it brittle, and the residual thermal stress will also cause micro cracks and reduce the mechanical properties. Moreover, the processed support needs a series of post-treatment, including cleaning, grinding, pickling, passivation, and finally electrochemical polishing. The process is cumbersome and time-consuming. These subsequent treatments will also lose part of the support, and the final yield is only about 70%, and about 30% of the loss means a huge loss.
In recent years, domestic and foreign enterprises have begun to adopt a new technology for bracket cutting, ultrafast laser, or ultrashort pulse laser. Its pulse width is only 10 picoseconds (10-12 seconds) to hundreds of femtoseconds (10-15 seconds), which can realize “cold” processing almost without thermal effect. Different from the melting mechanism of microsecond laser, the extremely high peak power brought by the ultra short pulse width of ultrafast laser will produce multiphoton absorption, skipping the melting process and directly evaporating the material. Therefore, ultrafast laser can process materials with relatively low energy, without residual heat and residue left on the materials, so as to achieve high-precision and clean processing, and many subsequent processes can be omitted. Generally speaking, the cleaned scaffold can be directly electrochemically polished; Due to the simplification of the manufacturing process, the yield can be increased to more than 90%.
 WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: Wechat
Wechat
Factors affecting the processing quality of laser cutting machine 2024-03-25
Laser cutting is a more common processing method in laser processing, and it is also a relatively simple one. The processing quality of the laser cutting machine is mainly reflected in the processing accuracy and surface quality, and the cutting surface quality is determined by …
Application of laser drilling machine in photovoltaic industry 2024-03-18
Laser drilling uses a high-energy-density laser beam to locally heat the material to a high enough temperature to evaporate, melt or vaporize it to form holes. The key to laser drilling lies in precise control of energy density, line speed and focus position to achieve precise p…
cutting machine manufacturers explain in detail the differences between ultraviolet, red light and green light sources? 2024-03-14
The most commonly used light sources for laser cutting machines are mainly red light, ultraviolet light, and green light. Each type of light source has different advantages. According to the characteristics, thickness and processing quality requirements of the processing materia…
Application and processing advantages of laser cutting machine in metal speaker mesh 2024-03-11
Metal speaker mesh is mainly used in sound-producing components of electronic equipment such as automobiles, mobile phones, and stereos. It is made of metal and has the characteristics of durability, good air permeability, etc. In the process of forming the metal speaker mesh, a…