What is a bioabsorbable stent ?
(Click 1,124 )The interventional treatment technology of coronary heart disease has been continuously improved, and the “bioabsorbable stent” is providing patients with rich and high-quality treatment options. Unlike traditional metal stents, bioabsorbable stents are made of polymer materials, which can be degraded into water and carbon dioxide after completing the mission of opening narrow blood vessels, and be absorbed by the human body, so as to restore normal physiological functions of blood vessels without leaving permanent metal implants in the body.
01 What is a bioabsorbable stent
A stent is a metal or polymer tube that is implanted into the lumen of any blood vessel or catheter to keep the channel unblocked. Scaffold materials are often used in surgical operations, such as vascular stents and intestinal stents that provide support, as well as artificial bone stents and artificial organ stents that serve as nutrient carriers and provide a certain size structure.
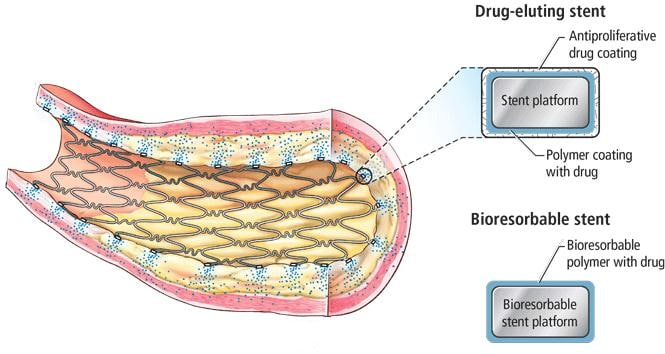
Traditional metal stents can provide permanent support for narrow blood vessels, but their long-term retention in the blood vessels will cause chronic damage to the blood vessels, which will lead to atrophy of the middle layer of blood vessels, aneurysm formation and reactive intimal hyperplasia, and eventually lead to vascular stenosis again. Compared with traditional metal stents, biodegradable stents have the advantages of low probability of blood vessel re-blocking, less adverse reactions, no need for long-term medication, and can be repeatedly placed, which can be divided into the following categories:
(1) Biodegradable vascular stent material
Vascular stent is a device that is put into human blood vessels or other conduits by surgery to expand blood vessels and prevent or reduce blockage. The traditional stent is made of metal, but it may form thrombus, hinder blood vessel reconstruction, and is unfavorable for multi-slice CT angiography. Biodegradable materials, such as polylactic acid, polyhydroxylic acid and polypeptide, which are embedded in collagen or gelatin protein or surface treated, are used for bioabsorbable scaffolds. Mazankowski Alberta Heart Research Institute, Alberta, Canada, is the first to successfully treat coronary artery disease using human absorbable vascular stent.
(2) Biodegradable nerve tissue scaffold
The tissue engineering scaffold materials for nerve repair are one kind of natural active materials derived from autologous nerves, skeletal muscles, blood vessels and membrane tubes, and the other kind is non-biological active materials, such as demineralized bone tubes, nylon fiber tubes, silica gel tubes, polyurethane, etc.
(3) Corneal tissue engineering scaffold
Corneal tissue engineering scaffold materials are required to be transparent, water absorbing, biodegradable, with certain mechanical strength and good refractive properties. In the past, the commonly used materials were HAMA and PMMA. In recent years, collagen and polyalkyd were mostly used.
(4) Other biodegradable scaffold materials
a. Natural degradable polymer materials
Natural biodegradable polymer material refers to the polymer degradable material extracted from animal and plant tissues, such as collagen, which itself is the tissue component of natural bone. Chitosan is a derivative of chitin, as well as gelatin, agar, dextran and hyaluronic acid. The characteristic of this kind of material is that the degradation products are easily absorbed by the body, but the strength and processing performance are poor, and the degradation rate cannot be adjusted.
b. Natural degradable inorganic materials
Coral is the skeleton of natural animals, 99% of which is calcium phosphate. Another example is coral hydroxyapatite (CHA), which has the porous structure of natural coral, has good porosity, and can adhere well to target cells without affecting proliferation, differentiation and osteogenesis. It is a good bone tissue engineering material.
c. Synthesis of degradable polymer materials
Common degradable synthetic polymer materials include polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, polycaprolactone, polyether, polycarbonate, etc. The degradation products of these materials can be metabolized and eliminated in the body, harmless to the body, and have good plasticity. Polylactic acid and polyglycolic acid are widely used in tissue engineering.
d. Synthesis of degradable inorganic materials
It mainly includes calcium phosphate water, hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, bioactive ceramics such as bioactive glass ceramics, extracellular matrix ceramics and other materials.
02 Advantages of bioabsorbable stent
(1) To avoid long-term retention of metal stent in coronary artery, which will affect the implementation of coronary artery surgical bypass.
(2) After the stent is absorbed, it can restore the normal vasodilation and contraction of blood vessels, which is beneficial to the positive remodeling of blood vessels.
(3) Interventional treatment can be repeated at the same site without the problems caused by stent overlap.
(4) It eliminates the “metallization” of coronary artery caused by too many stents.
(5) Avoid long-term oral antiplatelet drugs.
 WhatsApp:
WhatsApp: Wechat
Wechat
Femtosecond laser cutting machine reshapes the limit of ultra-precision manufacturing 2025-07-08
In the field of cutting-edge manufacturing that pursues micron or even nanometer precision, traditional processing methods have gradually reached physical limits. The emergence of femtosecond laser cutting machines, with its revolutionary "cold processing" characteristics brough…
Application of laser cutting machines in different fields of precision structural parts 2025-07-02
Electronic information field In the electronic information industry, the size of precision structural parts is getting smaller and smaller, but the precision requirements are getting higher and higher. Laser cutting machines play a key role in the processing of printed circuit …
Working principle and technical advantages of fiber laser cutting machine 2025-06-24
The working principle of fiber laser cutting machine is based on the high energy density characteristics of laser. The high-energy laser beam generated by the laser is focused on the surface of the workpiece through the optical focusing system, instantly heating the material to …
Application of fiber laser cutting machine in the manufacturing of agricultural machinery parts 2025-06-17
At the moment when agricultural mechanization is developing rapidly, fiber laser cutting machine has become a powerful assistant in the manufacturing of agricultural machinery parts with its unique advantages. It takes fiber laser as the core, outputs high-energy laser beam to m…